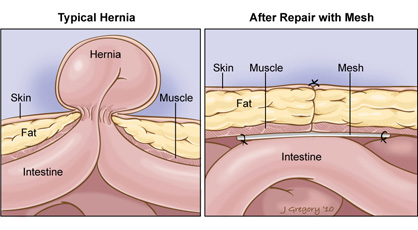
A hernia occurs when the contents of a body cavity bulge out of the area where they are normally contained. Dr Sanjoy Mandal, renowned Hernia surgeon in kolkata, says, these contents, usually the portions of intestine or abdominal fatty tissue, are enclosed in the thin membrane that naturally lines the inside of the cavity. Hernias by themselves may be asymptomatic (produce no symptoms) or cause slight to severe pain. Nearly all have a potential risk of having their blood supply cut off (becoming strangulated).
When the content of the hernia bulges out, the opening through which it bulges out can apply enough pressure so that blood vessels in the hernia are constricted and therefore the blood supply is cut off. If the blood supply is cut off at the hernia opening in the abdominal wall, it becomes a medical and surgical emergency as the tissue needs oxygen, which is transported by the blood supply.
Different types of abdominal hernia:
Inguinal (groin) hernia: Making up 75% of all abdominal wall hernias and occurring up to 25 times more often in men than women, these hernias are divided into two different types, direct and indirect. Both occur in the groin area where the skin of the thigh joins the torso (the inguinal crease), but they have slightly different origins. Both of these types of hernias can similarly appear as a bulge in the inguinal area. Distinguishing between the direct and indirect hernia, however, is important as a clinical diagnosis.
Indirect inguinal hernia: An indirect hernia follows the pathway that the testicles made during fetal development, descending from the abdomen into the scrotum. This pathway normally closes before birth but may remain a possible site for a hernia in later life. Sometimes the hernia sac may protrude into the scrotum. An indirect inguinal hernia may occur at any age.
Direct inguinal hernia: The direct inguinal hernia occurs slightly to the inside of the site of the indirect hernia, in an area where the abdominal wall is naturally slightly thinner. It rarely will protrude into the scrotum and can cause pain that is difficult to distinguish from testicle pain. Unlike the indirect hernia, which can occur at any age, the direct hernia tends to occur in the middle-aged and elderly because their abdominal walls weaken as they age.
Femoral hernia: The femoral canal is the path through which the femoral artery, vein, and nerve leave the abdominal cavity to enter the thigh. Although normally a tight space, sometimes it becomes large enough to allow abdominal contents (usually intestine) to protrude into the canal. A femoral hernia causes a bulge just below the inguinal crease, in roughly the mid-thigh area. Usually occurring in women, femoral hernias are particularly at risk of becoming irreducible (not able to be pushed back into place) and strangulated. Not all hernias that are irreducible are strangulated (have their blood supply cut off), but all hernias that are irreducible need to be evaluated by a hernia doctor in Kolkata.
Umbilical hernia: These common hernias (10%-30%) are often noted at birth as a protrusion at the belly button (the umbilicus). This is caused when an opening in the abdominal wall, which normally closes before birth, doesn’t close completely. If small (less than half an inch), this type of hernia usually closes gradually by age 2. Larger hernias and those that do not close by themselves usually require surgery between 2 to 4 years of age. Even if the area is closed at birth, umbilical hernias can appear later in life because this spot may remain a weaker place in the abdominal wall. Umbilical hernias can appear later in life or in women who are pregnant or who have given birth (due to the added stress on the area). They usually do not cause abdominal pain.
Incisional hernia: Abdominal surgery causes a flaw in the abdominal wall. This flaw can create an area of weakness through which a hernia may develop. This occurs after 2%-10% of all abdominal surgeries, although some people are more at risk. Even after surgical repair, incisional hernias may return.
Spigelian hernia: This rare hernia occurs along the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle through the Spigelian fascia, which is several inches lateral to the middle of the abdomen.
Obturator hernia: This extremely rare abdominal hernia develops mostly in women. This hernia protrudes from the pelvic cavity through an opening in the pelvic bone (obturator foramen). This will not show any bulge but can act like a bowel obstruction and cause nausea and vomiting. Because of the lack of visible bulging, this hernia is very difficult to diagnose.
Epigastric hernia: Occurring between the navel and the lower part of the rib cage in the midline of the abdomen, epigastric hernias are composed usually of fatty tissue and rarely contain intestine. Formed in an area of relative weakness of the abdominal wall, these hernias are often painless and unable to be pushed back into the abdomen when first discovered.
Hiatal hernia: This type of hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm. The diaphragm normally has a small opening for the esophagus. This opening can become the place where part of the stomach pushes through. Small Hiatal hernias can be asymptomatic (cause no symptoms), while larger ones can cause pain and heartburn.
All newly discovered hernias or symptoms that suggest you might have a hernia should prompt a visit to the doctor. Hernias, even those that ache, if not tender and easy to reduce (pushed back into the abdomen), are not necessarily surgical emergencies, but all have the potential to become serious. Referral to a Laparoscopic hernia surgeon in Kolkata should generally be made so that the need for surgery can be established and the procedure can be performed as elective surgery. This helps to avoid the risk of emergency surgery if your hernia becomes irreducible or strangulated.
If you find a new, painful, tender, and irreducible lump, it means that you may have an irreducible hernia, and you should have it checked in an emergency setting. If you already have a hernia and it suddenly becomes painful, tender, and irreducible, you should also go to the emergency department. Strangulation of intestine within the hernia sac can lead to gangrenous (dead) bowel in as little as six hours. Not all irreducible hernias are strangulated, but they need to be evaluated.
Procedure of Surgery: Advice by Hernia Surgeon
Hernia treatment consists of surgery unless you have medical conditions that preclude surgery. In some cases, belts or trusses can be used to temporarily hold the hernia in place.
In general, all hernias should be repaired unless severe pre-existing medical conditions make surgery unsafe. The possible exception to this is a hernia with a large opening. Trusses and surgical belts or bindings may help hold back the protrusion of selected hernias when hernia surgery in Kolkata is not possible or must be delayed. However, they should never be used in the case of femoral hernias.
Avoid activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure (lifting, coughing, or straining), which may cause the hernia to increase in size.